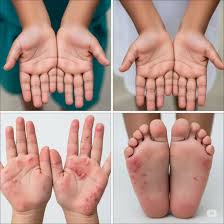
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease is a contagious viral infection caused most often by coxsackievirus. It spreads through direct contact with saliva, mucus, blister fluid, or contaminated surfaces. Close-contact environments, like a football team’s locker room, can allow the virus to move quickly between players.
“I got it but it was on my hands and I only had blisters, so it wasn’t that bad,” said junior Tannon Monden.
Symptoms of HFMD include fever, sore throat, and small red spots or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth. Infected individuals may also experience painful sores, loss of appetite, and fatigue. While the illness is generally mild, it spreads rapidly in groups that share equipment, towels, and water bottles.
“There was like 7 people on the team who got it,” said junior Jeremiah Howard
When HFMD appears on a sports team, it can significantly reduce attendance and participation. Sick players are advised to stay home to prevent further transmission, and equipment, benches, and common areas should be sanitized thoroughly. Preventative measures, including proper handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items, are essential to control outbreaks.
“I thought only little kids could get it but apparently not,” said senior Sam Hornbecker
Outbreaks among athletic teams highlight the importance of hygiene and awareness of contagious illnesses. Even when symptoms are mild, proper precautions can reduce the spread of HFMD and minimize disruptions to team activities.
“The disease spreads so fast and you have to wash your hands so much,” said sophomore Jesse Acton